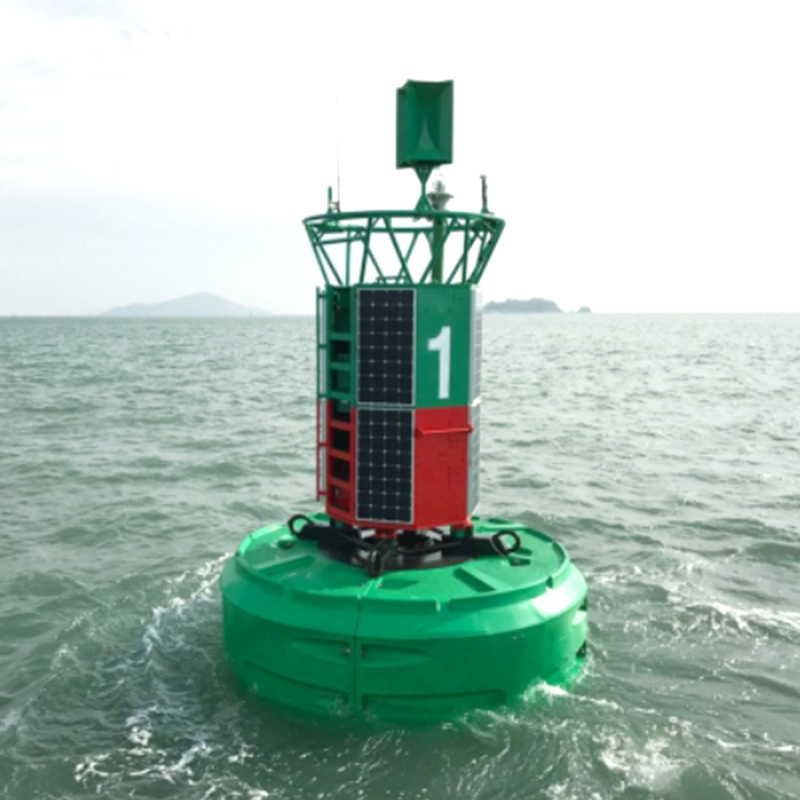
Why Choose a Rotomolding Fuel Tank Over Traditional Fuel Tanks?
In modern industrial, automotive, marine, and agricultural applications, fuel tanks are critical components for safety, efficiency, and reliability. Choosing the right manufacturing method significantly affects tank durability, cost, and design flexibility. Rotomolding fuel tanks, created through rotational molding, have gained popularity over traditional metal or blow-molded tanks. Below we explore why.
1. Superior Durability and Impact Resistance
Rotomolding Advantages
- Seamless Construction: Rotomolded fuel tanks are manufactured as one solid piece of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other thermoplastics. This eliminates welds, seams, or joints that could fail under stress.
- Flexibility: The plastic can absorb impacts and vibrations without cracking, unlike rigid metals.
- Resistance to Accidental Damage: Rotomolded tanks tolerate dents, drops, and minor collisions, making them ideal for off-road vehicles, industrial machinery, and marine applications.
Comparison to Traditional Tanks
- Steel Tanks: Strong but can dent or rust over time, especially in humid or marine environments.
- Aluminum Tanks: Lighter than steel but prone to fatigue cracks under repeated stress.
- Blow-Molded Plastic Tanks: Usually thinner and less impact-resistant, which can lead to stress cracking over time.
2. Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Attack
- Rotomolded tanks do not rust, unlike steel tanks, and resist chemical attack from fuel additives and environmental exposure.
- No additional coatings or liners are required, reducing maintenance costs.
- Metals, particularly steel, require protective coatings which can fail over time, leading to leaks or contamination.
Practical Benefit: For outdoor, marine, or industrial machinery exposed to moisture or corrosive fuels, rotomolded tanks provide long-lasting reliability without corrosion worries.
3. Design Flexibility
Complex Shapes and Customization
- Rotational molding allows manufacturers to produce tanks with integrated baffles, brackets, mounting flanges, and threaded ports without assembly.
- It supports non-standard shapes that fit into tight engine compartments or unusual vehicle layouts.
Weight Optimization
- Designers can vary wall thickness strategically, reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity.
- Lighter tanks improve vehicle fuel efficiency and reduce strain on mounting structures.
4. Seamless Construction Reduces Leakage Risk
- Traditional tanks often have welds or seams that may develop leaks over time.
- Rotomolded tanks are completely seamless, minimizing the risk of leakage even after years of use.
- Seamless design enhances safety when handling volatile fuels and reduces environmental contamination.
5. Cost-Effectiveness for Medium to Large Production Runs
Lower Tooling and Manufacturing Costs
- Rotomolding requires less expensive molds compared to metal stamping or blow molding for small and medium production runs.
- Ideal for custom designs or limited production batches without huge upfront costs.
Long-Term Savings
- Durability and corrosion resistance extend tank life, reducing replacement costs over time.
- Reduced maintenance due to seamless design and chemical resistance further improves cost-efficiency.
6. Enhanced Safety Features
- Rotomolded tanks can integrate internal baffles, which reduce fuel sloshing and improve vehicle stability.
- Baffles prevent fuel foam formation, ensuring accurate fuel level measurement and safer handling.
- Some designs can include reinforced areas for mounting fuel pumps, sending units, and sensors without compromising tank integrity.
7. Environmental and Regulatory Advantages
- Many rotomolding plastics are recyclable, which supports sustainability initiatives.
- Seamless, corrosion-resistant construction helps tanks meet strict safety, emission, and fuel containment regulations.
- Reduced leakage risk contributes to environmental protection in industrial and marine applications.
8. Rotomolding vs Traditional Fuel Tanks
| Feature | Rotomolding Fuel Tank | Steel Fuel Tank | Aluminum Fuel Tank | Blow-Molded Plastic Tank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Seamless, one-piece | Welded seams | Welded or riveted seams | Seamed sections |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Moderate | Moderate |
| Design Flexibility | High (complex shapes & baffles) | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Weight | Light | Heavy | Moderate | Light |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Moderate to high | Moderate | Moderate |
| Cost (Low/Medium Volume) | Moderate | High | High | Moderate |
| Fuel Sloshing Control | Easy (baffles integrated) | Requires separate installation | Requires separate installation | Limited |
| Lifespan | Long | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |


 English
English عربى
عربى