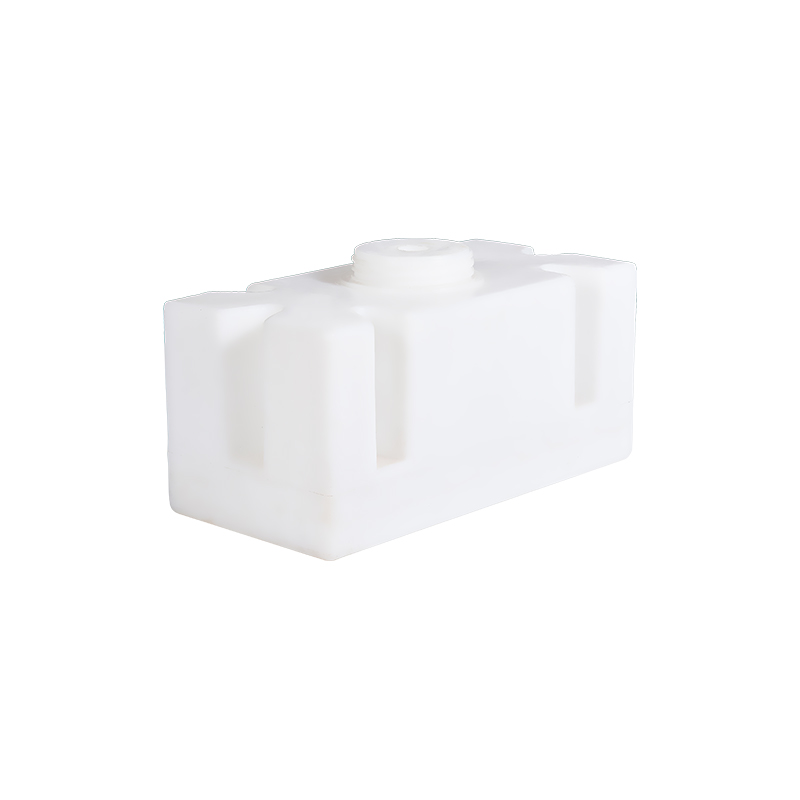
What is a rotary molded fuel tank? What advantages does it have over traditional fuel tanks?
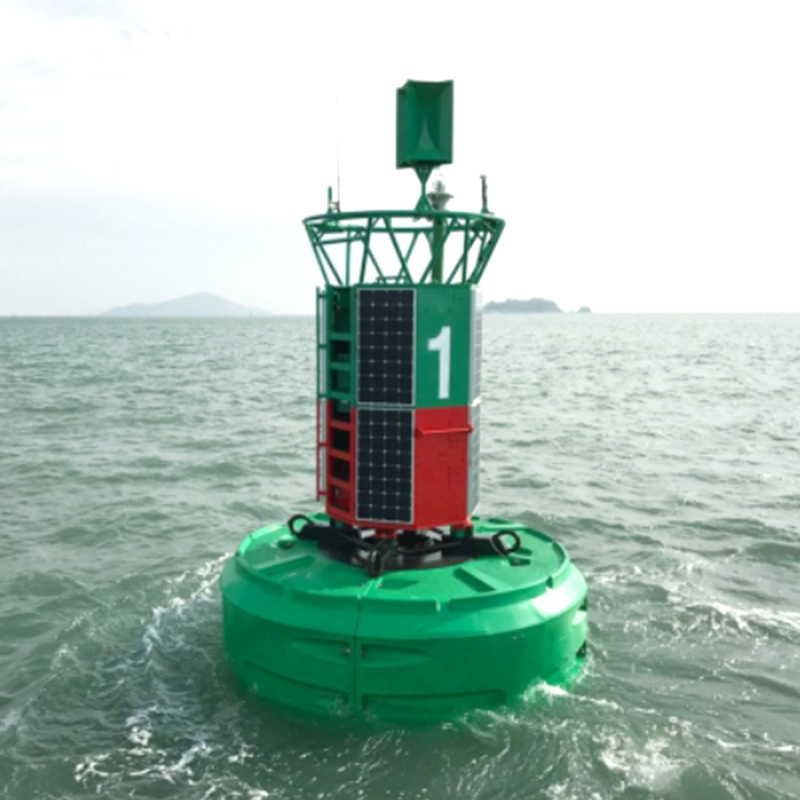
A rotomolding fuel tank is a fuel storage container produced using rotational molding technology. The basic principle of this process is to heat plastic pellets to a molten state and then place them in a rotating mold. As the mold rotates, the molten plastic evenly coats the inner walls of the mold, which is then cooled to form the final fuel tank. This process results in a fuel tank with uniform thickness, seamless structure, and high durability.
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods such as injection molding, blow molding, and metal welding, rotomolding fuel tanks offer several distinct advantages, particularly in terms of design flexibility, durability, safety, and cost efficiency.
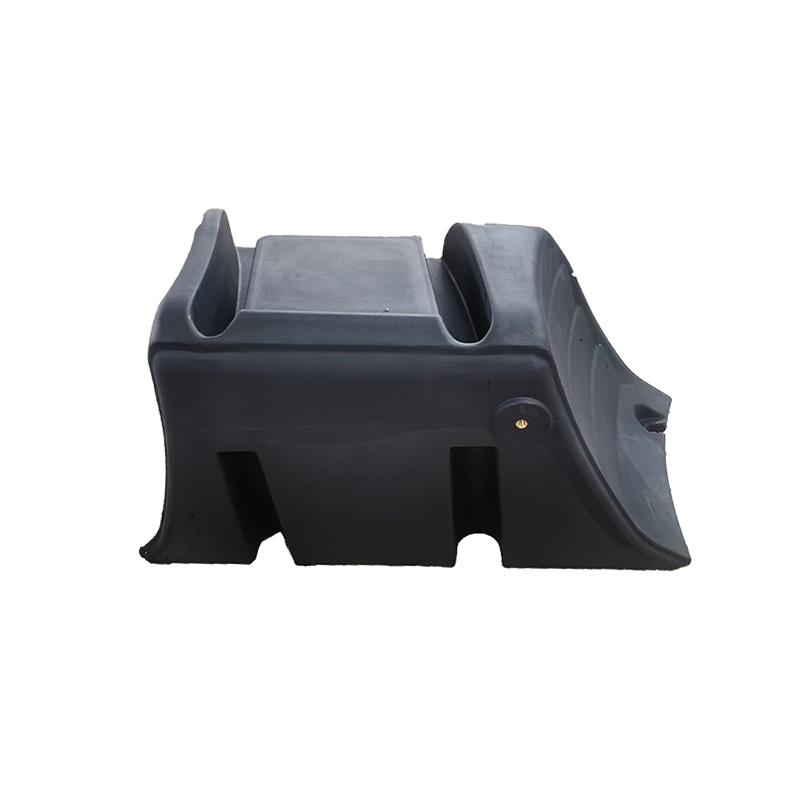

1. Greater Durability and Impact Resistance
The rotomolding process produces a uniform and robust plastic fuel tank, where the material is evenly distributed on the mold’s inner walls. As a result, the structure is stronger and more resistant to impacts compared to traditional fuel tanks. During vehicle or equipment use, fuel tanks are subjected to collisions or vibrations, and the rotomolded fuel tank is better equipped to handle these shocks.
Traditional fuel tanks (such as metal fuel tanks) often require welding to join several parts, which can create weak points susceptible to damage from impact. In contrast, the overall integrity and robust structure of rotomolded fuel tanks provide better resistance to damage during accidental impacts.
2. High Design Flexibility
Rotomolded fuel tanks offer high design flexibility, enabling the production of complex shapes and sizes. Since the rotational molding process does not rely on the shape limitations of traditional molds, it allows for fuel tanks to be customized to fit specific space requirements and design needs. This is particularly useful for applications that require precise fitting in vehicles, equipment, or special use cases.
For example, for narrow spaces or applications with intricate shapes, rotomolded fuel tanks can adapt more easily, while traditional fuel tanks are often constrained by mold shapes and cannot be as easily customized.
3. Seamless Structure
Traditional metal fuel tanks typically require welding to connect different parts, and each weld can potentially become a weak point where fuel leakage might occur. Rotomolded fuel tanks are made as a single, seamless piece, avoiding the risk of leakage that can arise from welded seams. This design not only reduces the likelihood of leaks but also eliminates weak points that could develop due to poor welds or external contaminants.
The seamless construction also improves the overall seal integrity, which is especially crucial in high-pressure environments. In contrast, welded seams in traditional fuel tanks can be prone to cracking or fatigue over time, increasing the risk of leaks.
4. Lighter Weight
Rotomolded fuel tanks are significantly lighter than traditional metal fuel tanks because they use relatively thin plastic walls, and plastic itself has a lower density than metals. The lightweight nature of plastic fuel tanks makes them ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in high-performance racing, motorcycles, or drones.
Reducing weight not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances the performance of the equipment. Metal fuel tanks, by comparison, add additional weight, which can reduce the overall efficiency and performance of the vehicle or machinery.
5. Better Corrosion Resistance
Rotomolded fuel tanks are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other corrosion-resistant plastic materials. These materials are highly resistant to the corrosive effects of fuels, chemicals, and environmental factors. In contrast, traditional metal fuel tanks are more susceptible to corrosion and rust, particularly in wet or marine environments, and require regular maintenance.
Polyethylene materials offer excellent chemical resistance, allowing them to withstand prolonged exposure to fuel without corrosion. Metal fuel tanks, however, can rust or corrode over time, especially when exposed to moisture, increasing the maintenance costs.
6. Lower Production Costs
The production cost of rotomolded fuel tanks is relatively low. The rotational molding process uses simpler molds and equipment, and the raw material cost is lower compared to metals. Furthermore, the production process is more straightforward, without the need for complex welding or high-pressure molding equipment. As a result, rotomolded fuel tanks are more cost-effective for large-scale production.
For traditional metal fuel tanks, the cost of materials (such as steel or aluminum) and welding equipment tends to be higher, making them more expensive to manufacture in comparison.
7. Environmentally Friendly
Many rotomolded fuel tanks are made from recyclable plastic materials, which are not only lightweight but also have high recyclability. In contrast, metal fuel tanks are more energy-intensive to produce and more challenging to recycle. As environmental regulations become stricter, rotomolded fuel tanks are increasingly seen as an environmentally friendly option.
8. Reduced Risk of Leaks and Seepage
Rotomolded fuel tanks’ seamless design and uniform thickness significantly reduce the risk of seepage and leakage. Traditional fuel tanks, with their welded seams, may have weak points where leaks could develop, especially under high stress. The absence of seams in rotomolded fuel tanks ensures better sealing and safety, especially during fuel storage and transportation.
Comparison Between Rotomolding Fuel Tanks and Traditional Fuel Tanks
| Feature | Rotomolding Fuel Tank (Rotomolding) | Traditional Fuel Tank (e.g., Metal Fuel Tank) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High impact resistance, uniform wall thickness, less likely to break | Can break or deform due to welded seams or corrosion |
| Design Flexibility | High, can be customized to fit specific spaces and shapes | Limited by mold and welding constraints |
| Welded Structure | Seamless design, reduces risk of leakage | Multiple welded seams, potential for leakage |
| Weight | Lighter, helps reduce vehicle or equipment weight | Heavier, adds to the overall load of the vehicle |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, resistant to chemicals and environmental factors | Susceptible to rust and corrosion, requires maintenance |
| Production Cost | Low, ideal for large-scale production | Higher, especially with metal and welding costs |
| Environmental Impact | Made from recyclable plastic, more eco-friendly | Difficult to recycle, energy-intensive production |
| Safety | High, uniform structure reduces risk of leaks | Welding seams may weaken, leading to leakage risks |


 English
English عربى
عربى