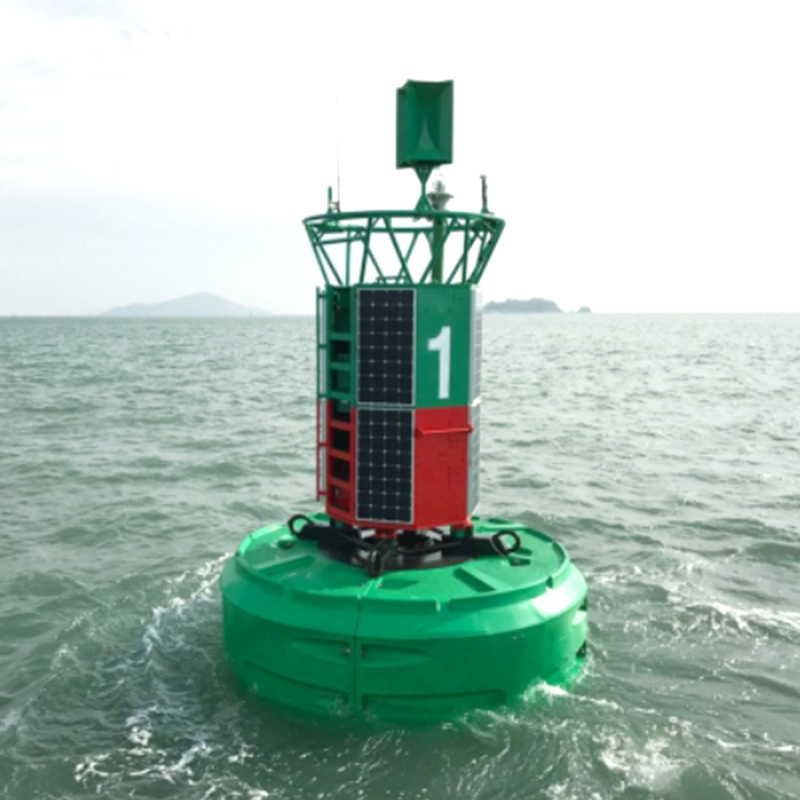
How Do Rotomolding Floating Docks Compare to Traditional Wooden Docks?
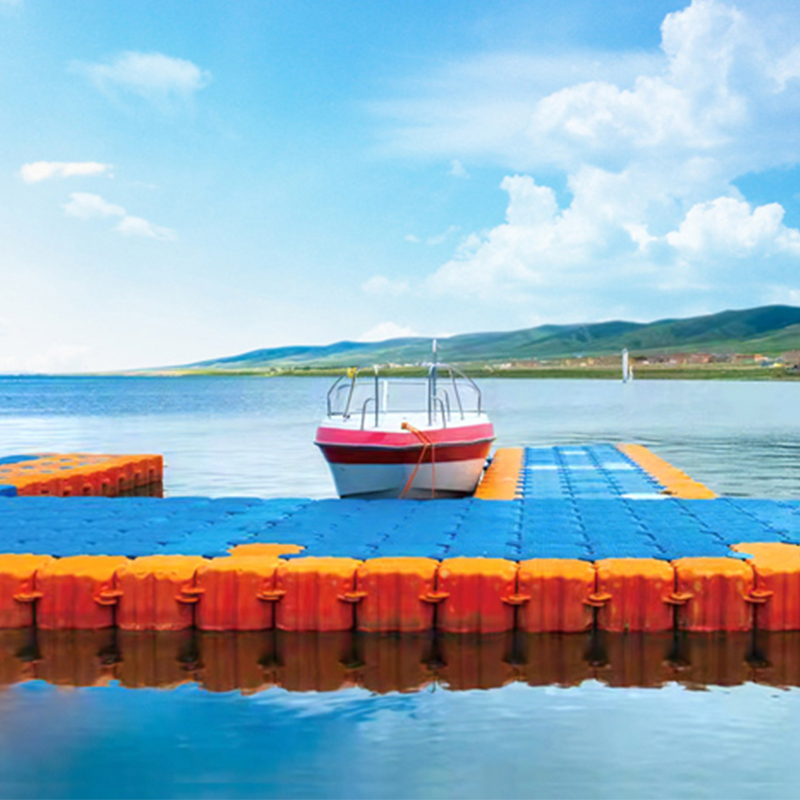
Floating docks are essential structures for a variety of waterfront applications, offering support for boats, water sports, and leisure activities. The material and construction methods used in their development significantly influence their performance, durability, and maintenance. Among the many materials used to build floating docks, Rotomolding Floating Docks and Traditional Wooden Docks are two popular options. While both serve similar purposes, they have distinct advantages and limitations.
1. Durability and Longevity
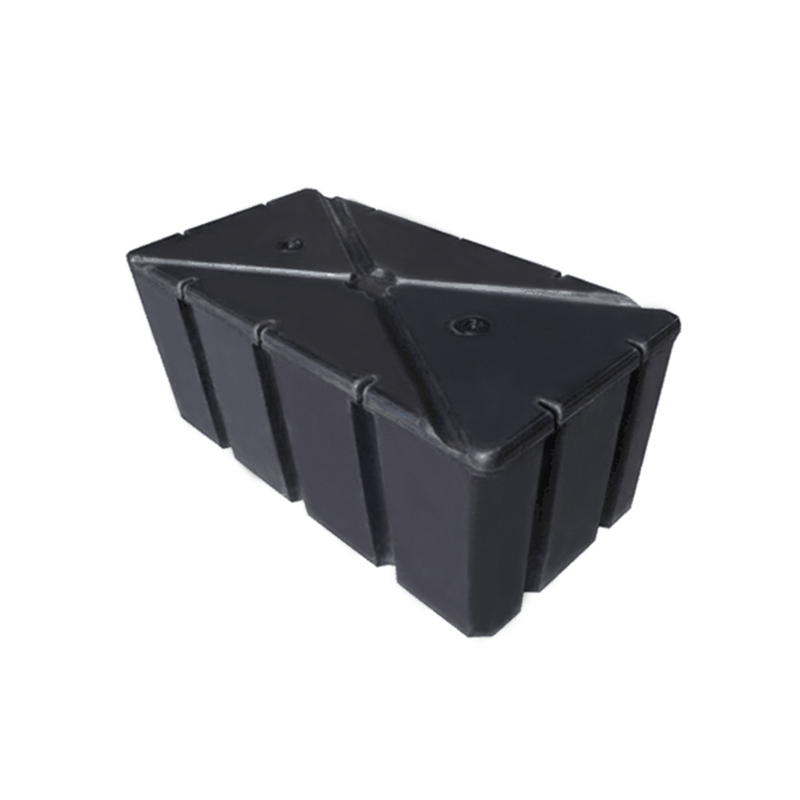
One of the most significant advantages of Rotomolding Floating Docks over Traditional Wooden Docks is the difference in durability and longevity. Rotomolding, or rotational molding, is a process where plastic materials, often high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are heated and molded into seamless, one-piece structures. This makes rotomolded floating docks highly resistant to water, salt, UV rays, and harsh weather conditions.
Rotomolding Floating Docks offer several benefits:
- Water Resistance: The materials used in rotomolding are waterproof, meaning these docks will not rot, warp, or deteriorate when exposed to water, unlike wood, which is highly susceptible to moisture-related damage.
- UV Resistance: Rotomolded docks are resistant to UV rays, preventing the material from fading, cracking, or becoming brittle. In contrast, wood docks often discolor and degrade due to constant sun exposure.
- Impact Resistance: The plastic material used in rotomolded docks is incredibly durable and capable of absorbing impact without cracking or splintering. Wooden docks, on the other hand, can be prone to splintering or breaking, especially in high-traffic areas.
On the other hand, Traditional Wooden Docks require regular upkeep and maintenance to prevent rot, mold, and decay. The natural fibers in wood can break down when exposed to water and the elements. Over time, the wood can splinter and crack, especially in high-moisture environments, making wooden docks less durable in comparison.
| Aspect | Rotomolding Floating Docks | Traditional Wooden Docks |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, no rot or swelling | Susceptible to water damage and rot |
| UV Resistance | UV-resistant, maintains color | Prone to fading and cracking |
| Impact Resistance | Highly resistant to impact | Prone to splintering and breaking |
2. Maintenance Requirements
When it comes to maintenance, Rotomolding Floating Docks provide a significant advantage over traditional wooden docks. Wooden docks require ongoing maintenance to ensure their longevity, especially in harsh or humid environments. These maintenance tasks can include:
- Sealing and Staining: Wooden docks must be sealed or stained regularly to protect them from moisture and UV damage. If this is not done, wood can become damaged by the elements.
- Cleaning: Wood can develop mold, mildew, or algae buildup, which requires frequent cleaning with chemical treatments.
- Repairs: Wood can splinter or crack, necessitating repairs or complete replacement of sections of the dock.
In contrast, Rotomolding Floating Docks are virtually maintenance-free. Once installed, these docks require little to no upkeep. The materials used are resistant to algae growth, mold, and mildew, and they do not need to be sealed, painted, or stained. Even in harsh environments, rotomolded docks retain their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for much longer.
| Maintenance Task | Rotomolding Floating Docks | Traditional Wooden Docks |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing/Staining | Not required | Required periodically |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, algae-resistant | Needs frequent cleaning |
| Repairs | Rarely needed | Regular repairs or replacement |
3. Weight and Buoyancy
Rotomolding Floating Docks are designed to be lightweight yet highly buoyant. The rotational molding process ensures that the plastic used for these docks has uniform thickness and is hollow inside, allowing for increased buoyancy. This design ensures that the dock remains afloat, even with heavy use, and provides excellent stability. Additionally, the lightweight nature of rotomolded docks makes them easier to transport and install.
Wooden docks, while capable of floating when constructed with proper flotation materials, can become much heavier when saturated with water. The inherent nature of wood allows it to absorb moisture, which can make the dock heavier over time, reducing its buoyancy. As a result, Rotomolding Floating Docks are typically more buoyant and stable, requiring less maintenance to maintain their performance in the water.
| Feature | Rotomolding Floating Docks | Traditional Wooden Docks |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to transport | Can become heavy over time |
| Buoyancy | Superior buoyancy | Buoyancy may decrease when wet |
4. Environmental Impact
Both Rotomolding Floating Docks and Traditional Wooden Docks have different environmental footprints. Rotomolded docks are often made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which is a recyclable material. At the end of their life cycle, rotomolded docks can be recycled or repurposed, reducing their environmental impact. The use of plastic also eliminates the need for wood harvesting, which helps preserve forests and minimizes habitat disruption.
In contrast, Traditional Wooden Docks are made from timber, which, while renewable, contributes to deforestation if the wood is not sourced sustainably. The chemicals used to treat wood (such as preservatives and paints) can also leach into the water, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. However, if the wood is sourced sustainably, the environmental impact can be minimized.
| Environmental Impact | Rotomolding Floating Docks | Traditional Wooden Docks |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sustainability | Made from recyclable HDPE | Wood is renewable, but sourcing can impact forests |
| Water Pollution | No harmful chemicals leach | Chemicals from treated wood may leach into water |
5. Cost Considerations
While the initial cost of Rotomolding Floating Docks may be higher than wooden docks, their long-term value and lower maintenance costs often make them a more cost-effective solution. Rotomolded docks have a longer lifespan, require minimal upkeep, and do not need to be replaced as frequently as wooden docks. Additionally, the reduced maintenance costs associated with rotomolded docks (no sealing, staining, or painting) make them an economically viable option in the long run.
Traditional Wooden Docks, while cheaper upfront, incur higher maintenance costs over time. Regular repairs, sealing, and staining can add up, making them more expensive to maintain over the life of the dock.
| Cost | Rotomolding Floating Docks | Traditional Wooden Docks |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance Cost | Low (minimal upkeep) | High (sealing, repairs, cleaning) |
| Long-Term Value | Cost-effective over time | Higher long-term costs due to maintenance |
FAQ
1. Are rotomolding floating docks better than wooden docks for environmental sustainability?
Yes, rotomolding floating docks tend to be more environmentally friendly as they are made from recyclable materials like HDPE, reducing deforestation and pollution. Additionally, they don’t require chemicals for preservation, unlike wooden docks that may leach harmful substances into the water.
2. How long do rotomolding floating docks last compared to wooden docks?
Rotomolding floating docks typically last much longer than wooden docks due to their resistance to rot, UV damage, and environmental wear. While wooden docks may need to be replaced or repaired after several years, rotomolded docks can last decades with minimal maintenance.
3. Do rotomolding floating docks require any maintenance?
No, rotomolding floating docks require very little maintenance. They do not need to be sealed, stained, or painted like wooden docks, and their smooth surfaces are resistant to algae and mold growth.
References
- “Durability of Rotomolded Docks vs. Wooden Docks,” Marine Structures Journal, 2022.
- “Environmental Impact of Floating Dock Materials,” Journal of Sustainable Marine Design, 2021.
- “The Long-Term Cost Benefits of Rotomolded Docks,” Coastal Infrastructure Review, 2020.


 English
English عربى
عربى