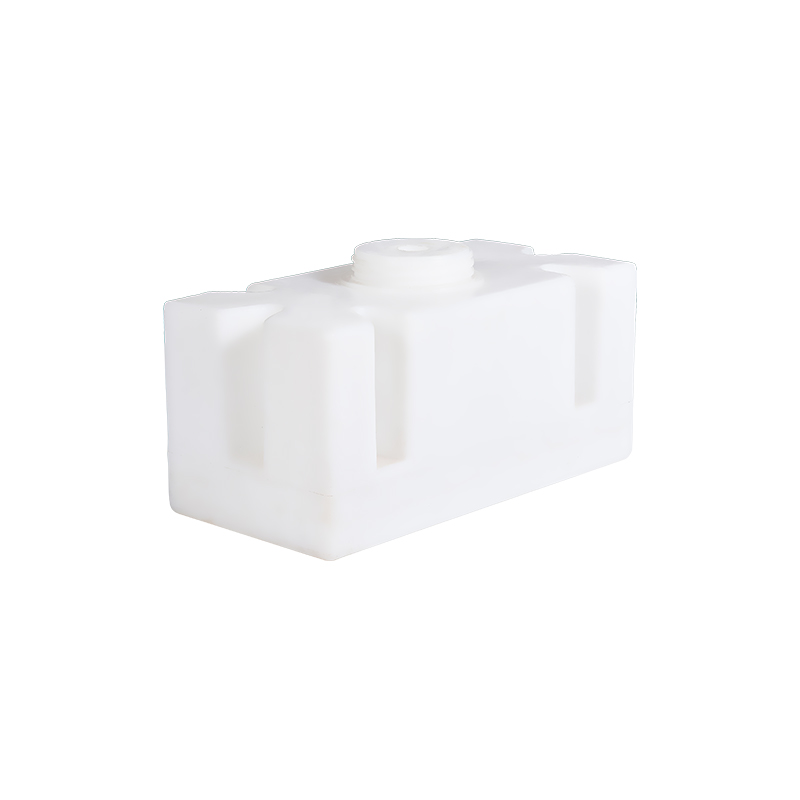
How Does the Durability of Rotomolded RV Water Tanks Compare to Traditional Tanks?
When it comes to choosing the best water tank for your RV, durability is one of the most crucial factors to consider. The reliability and lifespan of the tank will directly affect your water supply, which is essential for a comfortable and safe RV experience. Rotomolded RV water tanks have gained significant attention for their durability, but how do they compare to traditional options made of welded steel, fiberglass, or polyethylene?
What is Rotomolding?
Rotomolding, also known as rotational molding, is a manufacturing process that involves the use of a mold that is heated and rotated to evenly distribute the material (usually a plastic resin or powder) to form a part. This process results in seamless, one-piece tanks that are both highly durable and resistant to damage.
Rotomolding allows for the creation of complex shapes with a smooth finish, providing benefits in terms of strength, flexibility, and long-lasting performance. Rotomolded RV water tanks are known for their resistance to impacts, UV degradation, and cracking, making them ideal for the harsh environments RVs are often exposed to.
Traditional Water Tank Materials for RVs
In contrast, traditional RV water tanks have typically been made from materials such as welded steel, fiberglass, and polyethylene. Each of these materials has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, but when compared to rotomolded tanks, they often fall short in certain durability aspects.
Welded Steel Tanks
Welded steel tanks have been used for decades in RVs due to their strength and relatively low cost. However, steel is vulnerable to rust and corrosion, especially when exposed to water and moisture over time.
Fiberglass Tanks
Fiberglass tanks are known for being lightweight and durable. They are resistant to rust and corrosion, but they can be prone to cracks and chips, especially in extreme conditions or after impact.
Polyethylene Tanks
Polyethylene (PE) tanks are a popular choice due to their resistance to UV rays and corrosion. However, while they are relatively durable, they can still develop cracks under heavy stress and prolonged exposure to UV light.

Comparing Durability: Rotomolded vs. Traditional Tanks
Now that we understand the basics of rotomolded tanks and traditional tank materials, let’s explore how their durability compares in more detail.
1. Resistance to Impact and Cracking
Rotomolded Tanks
One of the standout features of rotomolded RV water tanks is their ability to withstand heavy impacts. The rotational molding process creates tanks that are seamless and free of weak points, making them highly resistant to cracks and splits. The even distribution of material during molding also ensures that the tank has consistent thickness throughout, which provides additional strength and durability. As a result, rotomolded tanks can absorb impacts from rough roads, bumps, and even minor collisions without breaking or cracking.
Traditional Tanks
Traditional materials, on the other hand, often have weaker points where cracks can form, especially in welded steel and fiberglass tanks. Steel tanks, while tough, can suffer from dents, rust, and corrosion, weakening the tank’s structure over time. Fiberglass tanks, while initially strong, may develop hairline cracks if subjected to repeated stress or impacts, and these cracks can expand over time. Polyethylene tanks are more resistant to impact than fiberglass but can still crack or become brittle under extreme pressure or low temperatures.
| Material | Impact Resistance | Cracking Susceptibility |
|---|---|---|
| Rotomolded Tanks | High (seamless construction absorbs impacts) | Very Low (no seams or joints to fail) |
| Steel Tanks | Moderate (can dent, rust, or corrode) | High (prone to rust and corrosion) |
| Fiberglass Tanks | Moderate (can crack or delaminate) | Moderate (prone to cracking and delamination) |
| Polyethylene Tanks | Moderate (resistant but can crack under extreme conditions) | Moderate (prone to cracking under stress) |
2. Resistance to UV Degradation
Rotomolded Tanks
Most rotomolded RV water tanks are made from UV-resistant materials, meaning they can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading. The smooth, seamless construction ensures that UV rays do not penetrate the tank, preventing brittleness and ensuring long-term performance. This feature is especially important for RV owners who frequently park their vehicles outdoors in sunny locations.
Traditional Tanks
While polyethylene tanks also have UV resistance, they are still prone to degradation over time, particularly if they are not treated with UV inhibitors. Fiberglass tanks are not inherently UV-resistant and can become brittle or fade when exposed to prolonged sunlight. Steel tanks are not affected by UV rays, but they can rust or corrode faster when exposed to moisture and air, especially at the welds.
3. Longevity and Lifetime
Rotomolded Tanks
Thanks to their robust construction and resistance to various environmental factors, rotomolded tanks tend to have a longer lifespan than traditional tanks. A well-maintained rotomolded RV water tank can last 20 years or more, making it an excellent long-term investment. The lack of seams or welds means fewer points of failure, and the material is resistant to rust, cracks, and leaks.
Traditional Tanks
The longevity of traditional tanks can vary significantly depending on the material:
- Steel tanks can last for many years, but they are prone to rust and corrosion, which can significantly reduce their lifespan.
- Fiberglass tanks can last 10-15 years, but cracking or delamination can cut their lifespan short.
- Polyethylene tanks typically last 10-20 years, but UV degradation and physical stress can accelerate wear and tear.
4. Weight and Ease of Maintenance
Rotomolded Tanks
Rotomolded tanks are typically lighter than steel tanks, making them easier to install and handle. They also require very little maintenance because they are resistant to rust, corrosion, and UV damage. The seamless design means there are no joints to inspect for leaks or wear. Regular cleaning and inspections are typically all that’s needed.
Traditional Tanks
Steel tanks are heavier, making them more difficult to install and requiring regular maintenance to check for rust and corrosion. Fiberglass tanks require inspection for cracks and delamination, while polyethylene tanks may need to be checked for cracks and UV damage.
5. Leak Resistance
Rotomolded Tanks
The seamless construction of rotomolded RV water tanks makes them highly resistant to leaks. Without any joints or seams, the possibility of a leak is virtually eliminated. Even if the tank is subjected to high stress or impacts, the material is unlikely to rupture, making it one of the most reliable options for water storage.
Traditional Tanks
Traditional tanks, especially those made from welded steel or fiberglass, are more prone to leaks due to welding points or joints that can deteriorate over time. Polyethylene tanks have fewer seams but can still develop cracks that lead to leaks, particularly if the tank is exposed to heavy physical stress.


 English
English عربى
عربى